This tutorial shows you how to develop a RESTful API in Node.js using the Express framework and an Oracle Database Cloud Service instance to deploy it in Oracle Application Container Cloud Service.
Express is a Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features to develop web and mobile applications. It facilitates a rapid development of Node based Web applications.
In this tutorial, you build a basic RESTful API that implements the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations on an employee table in a Oracle Database Cloud Service instance using plain Node.js and the Express framework.

The Node.js RESTful application responds to the following endpoints:
| Path | Description |
|---|---|
| GET: /employees | Gets all the employees. |
| GET: /employees// | Gets the employees that match the search criteria. |
| POST: /employees | Adds an employee. |
| PUT: /employees/ | Updates an employee. |
| DELETE: /employees/ | Removes an employee. |
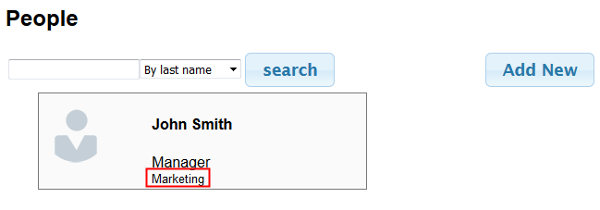
The HTML client to test the RESful API is provided in the next section (What do you need?) The zip file contains an index.html file and seven .png images. This client is developed using JQuery, Ajax and CSS.
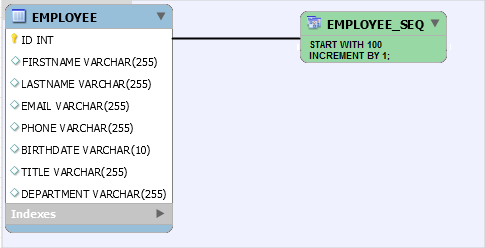
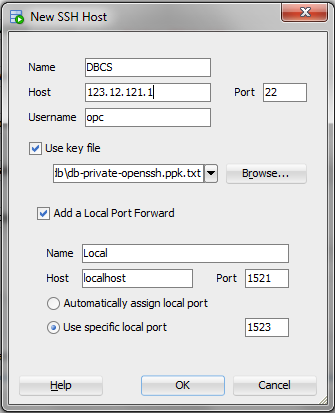
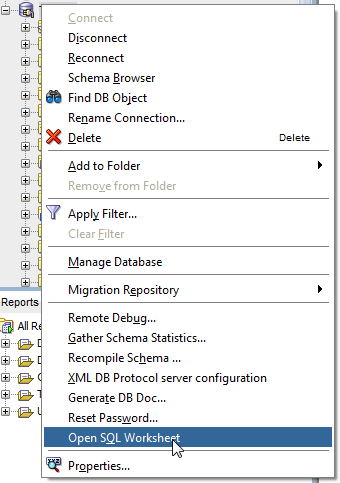
In this section, you create a connection to your Oracle Database Cloud Service instance from Oracle SQL Developer and execute the scripts to create the employee table and sequence and to insert a couple of employee rows.
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE ( ID INTEGER NOT NULL, FIRSTNAME VARCHAR(255), LASTNAME VARCHAR(255), EMAIL VARCHAR(255), PHONE VARCHAR(255), BIRTHDATE VARCHAR(10), TITLE VARCHAR(255), DEPARTMENT VARCHAR(255), PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); CREATE SEQUENCE EMPLOYEE_SEQ START WITH 100 INCREMENT BY 1;
 and then click Commit
and then click Commit  .
. , and then click Commit
, and then click Commit  .
.
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES (EMPLOYEE_SEQ.nextVal, 'Hugh', 'Jast', 'Hugh.Jast@example.com', '730-715-4446', '1970-11-28' , 'National Data Strategist', 'Mobility'); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES (EMPLOYEE_SEQ.nextVal, 'Toy', 'Herzog', 'Toy.Herzog@example.com', '769-569-1789','1961-08-08', 'Dynamic Operations Manager', 'Paradigm'); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES (EMPLOYEE_SEQ.nextVal, 'Reed', 'Hahn', 'Reed.Hahn@example.com', '429-071-2018', '1977-02-05', 'Future Directives Facilitator', 'Quality'); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES (EMPLOYEE_SEQ.nextVal, 'Novella', 'Bahringer', 'Novella.Bahringer@example.com', '293-596-3547', '1961-07-25' , 'Principal Factors Architect', 'Division'); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES (EMPLOYEE_SEQ.nextVal, 'Zora', 'Sawayn', 'Zora.Sawayn@example.com', '923-814-0502', '1978-03-18' , 'Dynamic Marketing Designer', 'Security'); In this section, you create the REST Service and you use the NPM utility to download and build dependencies for your Node.js project.
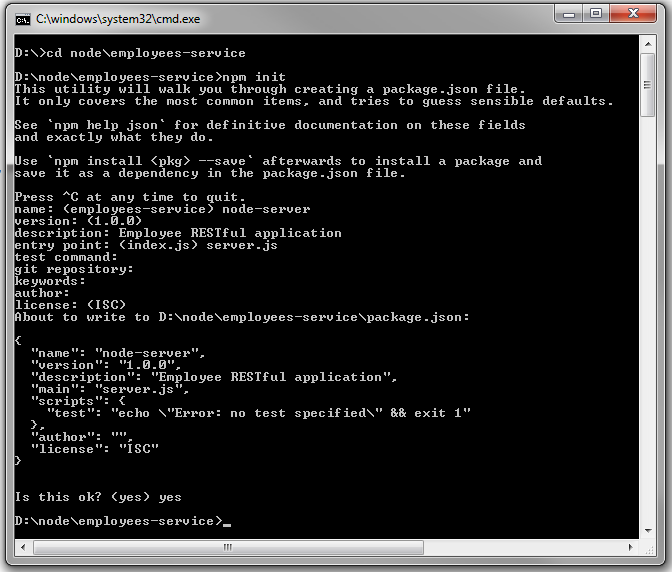
The package.json file is created and stored in the current folder. You can open it and modify it, if needed.
npm install --save express
In the console window, install the body-parser dependency:
npm install --save body-parser
The body-parser dependency is a Node.js middleware for handling JSON, Raw, Text and URL encoded form data. Note: If the console displays optional, dep failed or continuing output, ignore it. The output pertains to warnings or errors caused by dependencies on native binaries that couldn't be built. The libraries being used often have a JavaScript fallback node library, and native binaries are used only to optimize performance. Open the generated package.json file in a text editor, and verify its contents. It should look like this:
< "name": "node-server", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "Employee RESTful application", "main": "server.js", "scripts": < "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1", "start": "node server.js" >, "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": < "body-parser": "^1.14.1", "express": "^4.13.3" >> var express = require('express'); var bodyParser = require('body-parser'); var oracledb = require('oracledb');var PORT = process.env.PORT || 8089;var app = express();var connectionProperties = < user: process.env.DBAAS_USER_NAME || "oracle", password: process.env.DBAAS_USER_PASSWORD || "oracle", connectString: process.env.DBAAS_DEFAULT_CONNECT_DESCRIPTOR || "localhost/xe" >;function doRelease(connection) < connection.release(function (err) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); >>); >// configure app to use bodyParser() // this will let us get the data from a POST app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded(< extended: true >)); app.use(bodyParser.json(< type: '*/*' >));var router = express.Router();router.use(function (request, response, next) < console.log("REQUEST:" + request.method + " " + request.url); console.log("BODY:" + JSON.stringify(request.body)); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*'); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE'); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With,content-type'); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', true); next(); >);/** * GET / * Returns a list of employees */ router.route('/employees/').get(function (request, response) < console.log("GET EMPLOYEES"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >console.log("After connection"); connection.execute("SELECT * FROM employee",<>, < outFormat: oracledb.OBJECT >, function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error getting data from DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >console.log("RESULTSET:" + JSON.stringify(result)); var employees = []; result.rows.forEach(function (element) < employees.push(< id: element.ID, firstName: element.FIRSTNAME, lastName: element.LASTNAME, email: element.EMAIL, phone: element.PHONE, birthDate: element.BIRTHDATE, title: element.TITLE, dept: element.DEPARTMENT >); >, this); response.json(employees); doRelease(connection); >); >); >);/** * GET /searchType/searchValue * Returns a list of employees that match the criteria */ router.route('/employees/:searchType/:searchValue').get(function (request, response) < console.log("GET EMPLOYEES BY CRITERIA"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >console.log("After connection"); var searchType = request.params.searchType; var searchValue = request.params.searchValue; connection.execute("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE "+searchType+" = :searchValue",[searchValue], < outFormat: oracledb.OBJECT >, function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error getting data from DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >console.log("RESULTSET:" + JSON.stringify(result)); var employees = []; result.rows.forEach(function (element) < employees.push(< id: element.ID, firstName: element.FIRSTNAME, lastName: element.LASTNAME, email: element.EMAIL, phone: element.PHONE, birthDate: element.BIRTHDATE, title: element.TITLE, dept: element.DEPARTMENT >); >, this); response.json(employees); doRelease(connection); >); >); >); /** * POST / * Saves a new employee */ router.route('/employees/').post(function (request, response) < console.log("POST EMPLOYEE:"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >var body = request.body; connection.execute("INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT)"+ "VALUES(EMPLOYEE_SEQ.NEXTVAL, :firstName,:lastName,:email,:phone,:birthdate,:title,:department)", [body.firstName, body.lastName, body.email, body.phone, body.birthDate, body.title, body.dept], function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error saving employee to DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >response.end(); doRelease(connection); >); >); >);/** * PUT / * Update a employee */ router.route('/employees/:id').put(function (request, response) < console.log("PUT EMPLOYEE:"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >var body = request.body; var connection.execute("UPDATE EMPLOYEE SET FIRSTNAME=:firstName, LASTNAME=:lastName, PHONE=:phone, BIRTHDATE=:birthdate,"+ " TITLE=:title, DEPARTMENT=:department, EMAIL=:email WHERE [body.firstName, body.lastName,body.phone, body.birthDate, body.title, body.dept, body.email, id], function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error updating employee to DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >response.end(); doRelease(connection); >); >); >);/** * DELETE / * Delete a employee */ router.route('/employees/:id').delete(function (request, response) < console.log("DELETE EMPLOYEE ID:"+request.params.id); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >var body = request.body; var connection.execute("DELETE FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE [id], function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error deleting employee to DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >response.end(); doRelease(connection); >); >); >);app.use(express.static('static')); app.use('/', router); app.listen(PORT);The completed server.js should look like this:
var express = require('express'); var app = express(); var bodyParser = require('body-parser'); var oracledb = require('oracledb'); oracledb.autoCommit = true; var connectionProperties = < user: process.env.DBAAS_USER_NAME || "oracle", password: process.env.DBAAS_USER_PASSWORD || "oracle", connectString: process.env.DBAAS_DEFAULT_CONNECT_DESCRIPTOR || "129.152.132.76:1521/ORCL" >; function doRelease(connection) < connection.release(function (err) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); >>); > // configure app to use bodyParser() // this will let us get the data from a POST app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded(< extended: true >)); app.use(bodyParser.json(< type: '*/*' >)); var PORT = process.env.PORT || 8089; var router = express.Router(); router.use(function (request, response, next) < console.log("REQUEST:" + request.method + " " + request.url); console.log("BODY:" + JSON.stringify(request.body)); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*'); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE'); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With,content-type'); response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', true); next(); >); /** * GET / * Returns a list of employees */ router.route('/employees/').get(function (request, response) < console.log("GET EMPLOYEES"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >console.log("After connection"); connection.execute("SELECT * FROM employee",<>, < outFormat: oracledb.OBJECT >, function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error getting data from DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >console.log("RESULTSET:" + JSON.stringify(result)); var employees = []; result.rows.forEach(function (element) < employees.push(< id: element.ID, firstName: element.FIRSTNAME, lastName: element.LASTNAME, email: element.EMAIL, phone: element.PHONE, birthDate: element.BIRTHDATE, title: element.TITLE, dept: element.DEPARTMENT >); >, this); response.json(employees); doRelease(connection); >); >); >); /** * GET /searchType/searchValue * Returns a list of employees that match the criteria */ router.route('/employees/:searchType/:searchValue').get(function (request, response) < console.log("GET EMPLOYEES BY CRITERIA"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >console.log("After connection"); var searchType = request.params.searchType; var searchValue = request.params.searchValue; connection.execute("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE "+searchType+" = :searchValue",[searchValue], < outFormat: oracledb.OBJECT >, function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error getting data from DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >console.log("RESULTSET:" + JSON.stringify(result)); var employees = []; result.rows.forEach(function (element) < employees.push(< id: element.ID, firstName: element.FIRSTNAME, lastName: element.LASTNAME, email: element.EMAIL, phone: element.PHONE, birthDate: element.BIRTHDATE, title: element.TITLE, dept: element.DEPARTMENT >); >, this); response.json(employees); doRelease(connection); >); >); >); /** * POST / * Saves a new employee */ router.route('/employees/').post(function (request, response) < console.log("POST EMPLOYEE:"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >var body = request.body; connection.execute("INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT)"+ "VALUES(EMPLOYEE_SEQ.NEXTVAL, :firstName,:lastName,:email,:phone,:birthdate,:title,:department)", [body.firstName, body.lastName, body.email, body.phone, body.birthDate, body.title, body.dept], function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error saving employee to DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >response.end(); doRelease(connection); >); >); >); /** * PUT / * Update a employee */ router.route('/employees/:id').put(function (request, response) < console.log("PUT EMPLOYEE:"); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >var body = request.body; var connection.execute("UPDATE EMPLOYEE SET FIRSTNAME=:firstName, LASTNAME=:lastName, PHONE=:phone, BIRTHDATE=:birthdate,"+ " TITLE=:title, DEPARTMENT=:department, EMAIL=:email WHERE [body.firstName, body.lastName,body.phone, body.birthDate, body.title, body.dept, body.email, id], function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error updating employee to DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >response.end(); doRelease(connection); >); >); >); /** * DELETE / * Delete a employee */ router.route('/employees/:id').delete(function (request, response) < console.log("DELETE EMPLOYEE ID:"+request.params.id); oracledb.getConnection(connectionProperties, function (err, connection) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error connecting to DB"); return; >var body = request.body; var connection.execute("DELETE FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE [id], function (err, result) < if (err) < console.error(err.message); response.status(500).send("Error deleting employee to DB"); doRelease(connection); return; >response.end(); doRelease(connection); >); >); >); app.use(express.static('static')); app.use('/', router); app.listen(PORT); In this section, you add the client files to your project and you update the index.html file to connect the client to your RESTful application.
https://employees-service-identity-domain.apaas.us2.oraclecloud.com To ensure that your server application runs correctly in the cloud, you must:
When you upload your application to Oracle Application Container Cloud Service using the user interface, you must include a file called manifest.json in the application archive ( .zip, .tgz, .tar.gz file). If you use the REST API to upload the application, this file is still required but doesn’t have to be in the archive.
< "runtime":< "majorVersion":"4" >, "command": "node server.js", "release": <>, "notes": "" >In the deployment.json file you can specify how much memory to allocate to your application, how many application instances to create initially, additional environment variables, and service bindings to other Oracle Cloud services. For this tutorial you create the deployment.json file to add the Oracle Database Cloud Service binding.
Note: If you don't specify the values or the file is omitted, memory and instance defaults are used.
Before you can deploy your application, you must copy it to the storage service. You need your Oracle Cloud service credentials (username, password, identity domain) to use the REST API. With your credentials, you create cURL scripts to upload your application to the storage service.
curl -i -X PUT \ -u Username:Password \ https://hostname/v1/Storage-Identity-Domain/ employees-service curl -i -X PUT \ -u Username:Password \ https://hostname/v1/Storage-Identity-Domain/employees-service/node-employees-service.zip -T Path-to-local-file>/node-employees-service.zip To deploy your application, you need to include standard information in your script. The following example script shows placeholders for the required information:
url -i -X POST \ -u Username:Password \ -H "X-ID-TENANT-NAME:Identity-Domain" \ -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" \ -F "name=employees-service" \ -F "runtime=node" \ -F "subscription=Monthly" \ -F "deployment=Path-to-local-file/deployment.json" \ -F "archiveURL=employees-service/node-employees-service.zip" \ -F "notes=Node employees REST service application" \ https://hostname/paas/service/apaas/api/v1.1/apps/Identity-Domain Here are a few key points about this example:
https://employees-service-identity-domain.apaas.us2.oraclecloud.com/employees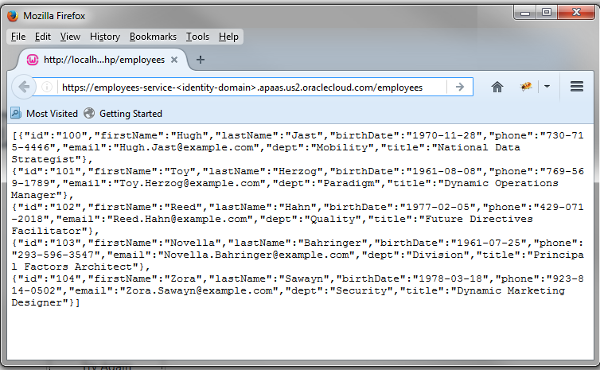
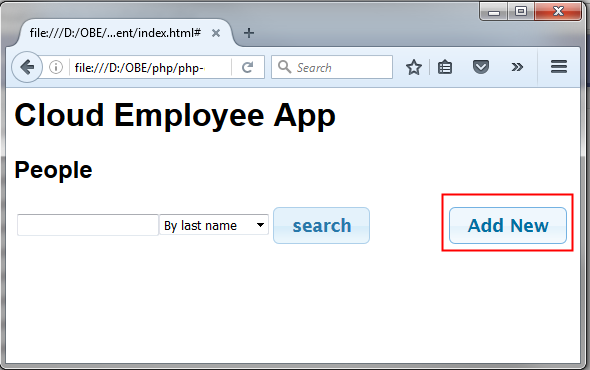
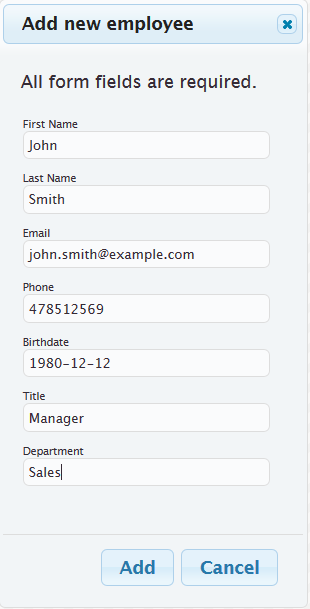
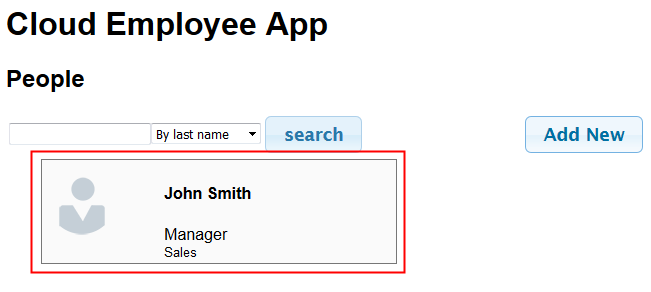
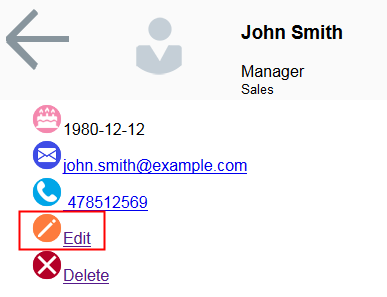
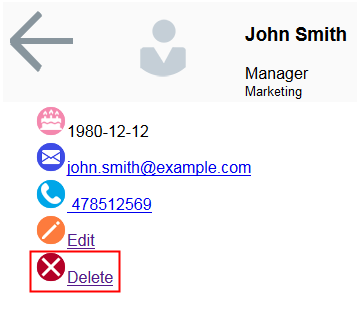
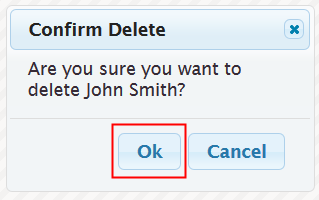
 The employee card is updated.
The employee card is updated.